What is enterprise risk management?
Enterprise risk management ensures that management has in place a process to set objectives and that the chosen objectives support and align with the entity’s mission and are consistent with its risk appetite.
What are the objectives of enterprise risk management?
The objectives of ERM include: Identifying and assessing a broad array of risks that could negatively impact the achievement of institutional goals and objectives. Ensuring appropriate ownership and accountability of risks. Developing and implementing appropriate risk mitigation and monitoring plans by risk owners.
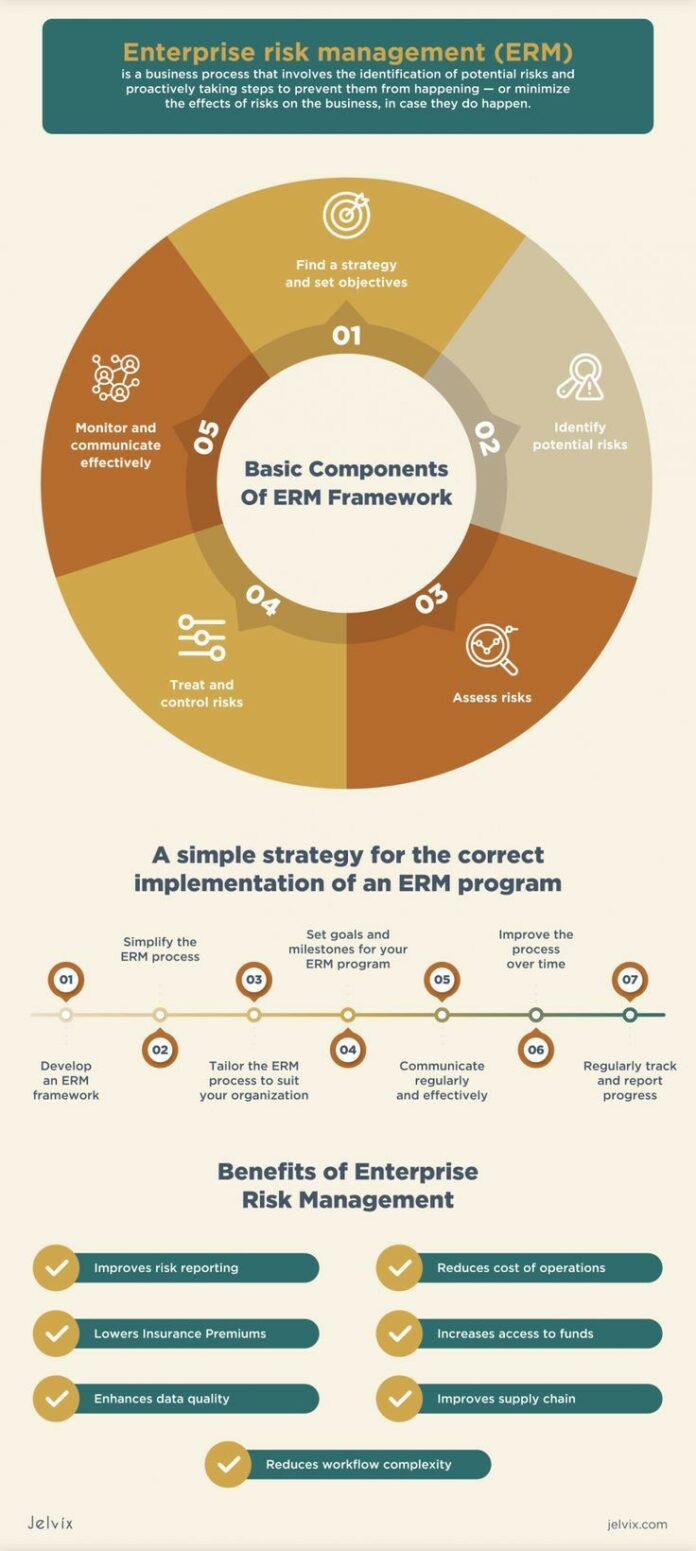
What are the 8 components of ERM?
The COSO framework for ERM identifies eight components:
- Internal environment
- Objective setting
- Event identification
- Risk assessment
- Risk response
- Control activities
- Information & communication
- Monitoring
Who is responsible for ERM process?
While departmental roles differ among businesses, most companies place ultimate responsibility for ERM with their Board of Directors. A culture of risk management, after all, must start at the top.
What is the difference between ERM and risk management?
Some commentators pin the difference on timing: traditional risk management “typically only occurs after an incident has already happened and is done to prevent that situation from happening again.â€
ERM, conversely, is future-looking, and “attempts to determine potential events and situations that could, or are even likely to, occur.â€
TRM tends to focus on risk avoidance, while ERM takes stock of potential risks and identifies which ones are worth taking, therefore focusing more on opportunity alongside pure risk.
And as we noted above, ERM encompasses the entire enterprise; and is top-down, whereas traditional risk management may focus on only one area, and not emanate from a holistic view of the entire organization.
Because traditional risk management (TRM) is well established and routinely practiced across businesses, it has become quite standardized. ERM is more dynamic, agile and adaptable to situations or organizations. Of the two, ERM is recognized as “far and away the more fluid, adaptable, and dynamic of the two methods.â€