Introduction to Risk Management: Principles and Guidelines
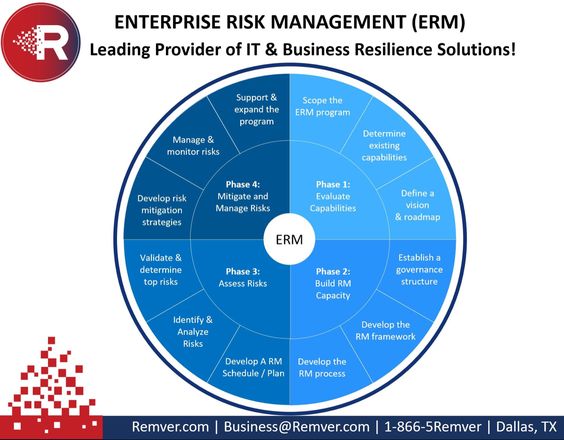
Risk management is an essential process for any organization, helping to identify, assess, and prioritize potential risks and develop effective strategies for managing them. This article will provide an overview of the key principles and guidelines for risk management.
Risk Identification
The first step in effective risk management is identifying potential risks, which can include anything from financial risks to reputational risks. This section explores some of the key methods for identifying risks, such as risk mapping and scenario analysis.
Risk Assessment
Once potential risks have been identified, the next step is to assess their likelihood and potential impact. This section outlines some of the most common methods for risk assessment, such as qualitative and quantitative risk analysis.
Risk Treatment
Once risks have been assessed, the next step is to develop strategies for treating them. This section explores some of the most common risk treatment options, such as risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk transfer, and risk acceptance.
Risk Monitoring and Review
Effective risk management requires ongoing monitoring and review, to ensure that risk treatment strategies remain effective and that new risks are identified and addressed. This section explores some of the key methods for risk monitoring and review, such as risk reporting and performance metrics.
Risk Communication
Risk communication is a critical component of effective risk management, enabling organizations to share information about potential risks and risk treatment strategies with stakeholders. This section explores some of the key principles of risk communication, such as transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Risk Culture
An effective risk management culture is essential for ensuring that risk management processes are integrated into the organization’s daily operations. This section explores some of the key principles of risk culture, such as leadership and accountability.
Risk Management Frameworks
There are many risk management frameworks available to organizations, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. This section explores some of the most common risk management frameworks, such as ISO 31000 and COSO.
Continuous Improvement
Effective risk management requires ongoing improvement and adaptation to changing circumstances. This section explores some of the key principles of continuous improvement in risk management, such as learning from experience and staying up-to-date with emerging risks.
You might find these FREE courses useful
Conclusion
Risk management is a complex and dynamic process, requiring organizations to be proactive, adaptable, and collaborative. By following the key principles and guidelines outlined in this article, organizations can develop effective risk management strategies that help them achieve their goals and protect their stakeholders.